Oxygen-containing Compounds
Keywords:
- Alcohols
- Important reactions
- Dehydrations (formation of carbocations)
- Substitution reactions (SN1 or SN2
depending on alcohol and derived product)
- General principles
- Hydrogen bonding
- Effect of chain branching on physical properties
- Aldehydes and ketones
- Important reactions
- Nucleophilic addition reactions at C=O bond
- Acetal, ketal, hemiacetal, hemiketal
- Imine, enamine
- Reactions at adjacent positions
- Aldol condensation
- Keto-enol tautomerism
- General principles
- Effect of substituents on reactivity of C=O
- Steric hindrance
- Acidity of
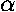 -H
-H
- Carbanions
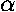 ,
,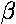 unsaturated carbonyls
unsaturated carbonyls
- Carboxylic acids
- Important carboxyl group reactions
- Decarboxylation
- Esterification
- General principles
- H bonding
- Inductive effect of substituents
- Resonance stability of carboxylate anion
- Common acid derivatives (acid chlorides, anhydrides, amides,
esters, keto acids)
- Important reactions
- Hydrolysis of fats and glycerides (saponification)
- Hydrolysis of amides
- General principles
- Relative reactivity of acid derivatives
- Steric effects
- Ethers
- Cleavage by acid
- Weak basicity of ethers
- Phenols
- Geenral principles
- Effects of substituents on acidity
- Hydrogen bonding
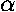 -H
-H
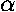 ,
,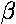 unsaturated carbonyls
unsaturated carbonyls